Setup Amazon FSx for OpenZFS with AWS ParallelCluster 🗂

FSx OpenZFS is a new filesystem offering that provides a managed OpenZFS filesystem. In previous blogposts we’ve showed how to use FSx Lustre, FSx Netapp Ontap and EFS with AWS ParallelCluster. In this blogpost we’ll show you how to create and mount OpenZFS filesystems on ParallelCluster. Before we start, when should you use OpenZFS?
So when should you use FSx OpenZFS?
- NFS compliant filesystem
- Fast filesystem performance for 30% cheaper than FSx Lustre
- Built in support for backups
- Multi-AZ support
So when shouldn’t you use FSx OpenZFS?
- Syncing data from a S3 Bucket in the same region. There’s no native S3 integration, just use FSx Lustre.
Setup
From the FSx OpenZFS docs we learn that the following ports are required:
| Protocol | Ports | Role |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 111 | Remote procedure call for NFS |
| UDP | 111 | Remote procedure call for NFS |
| TCP | 2049 | NFS server daemon |
| UDP | 2049 | NFS server daemon |
| TCP | 20001 - 20003 | NFS mount, status monitor, and lock daemon |
| UDP | 20001 - 20003 | NFS mount, status monitor, and lock daemon |
So we’ll need to:
- Create the Security Group
- Create the filesystem & associate the security group
- Create a cluster that mounts the filesystem
Since OpenZFS is built with NFS support, it requires no extra installation in AWS ParallelCluster image. We just need to mount the filesystem.
1. Create Security Group
-
Create a new Security Group by going to Security Groups > Create Security Group:
- Name
FSx OpenZFS - Description
Allow FSx OpenZFS to mount to ParallelCluster - VPC
Same as pcluster vpc
- Name
-
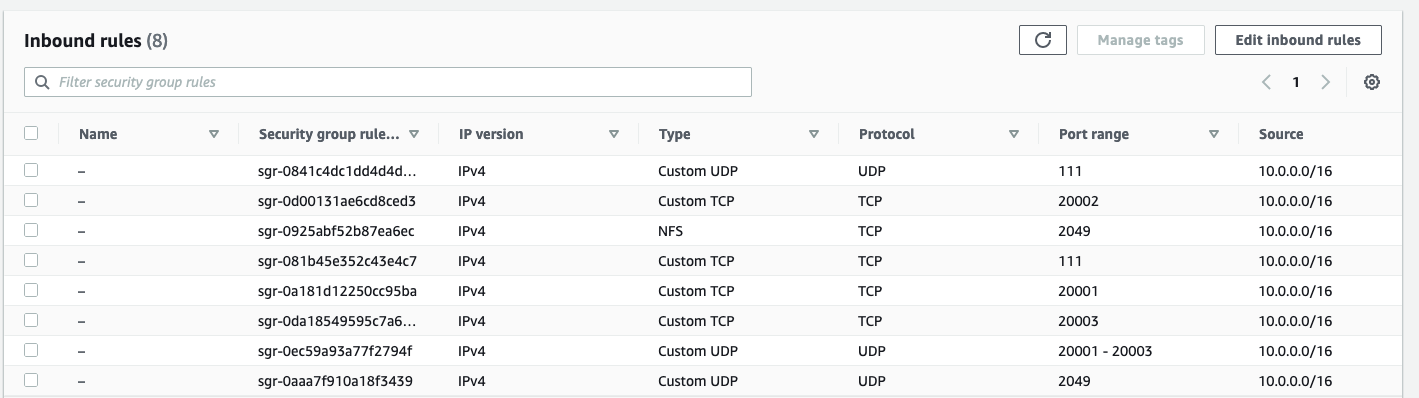
Create new Inbound Rules, one for each port:
Protocol Ports Role TCP 111 Remote procedure call for NFS UDP 111 Remote procedure call for NFS TCP 2049 NFS server daemon UDP 2049 NFS server daemon TCP 20001 - 20003 NFS mount, status monitor, and lock daemon UDP 20001 - 20003 NFS mount, status monitor, and lock daemon i.e.
- Custom TCP
- Port
111 - Same CIDR as the VPC
10.0.0.0/16
-
Leave Outbound Rules as the default:
2. Create FSx OpenZFS
-
Go to the Amazon Console and click Create FSx OpenZFS.
-
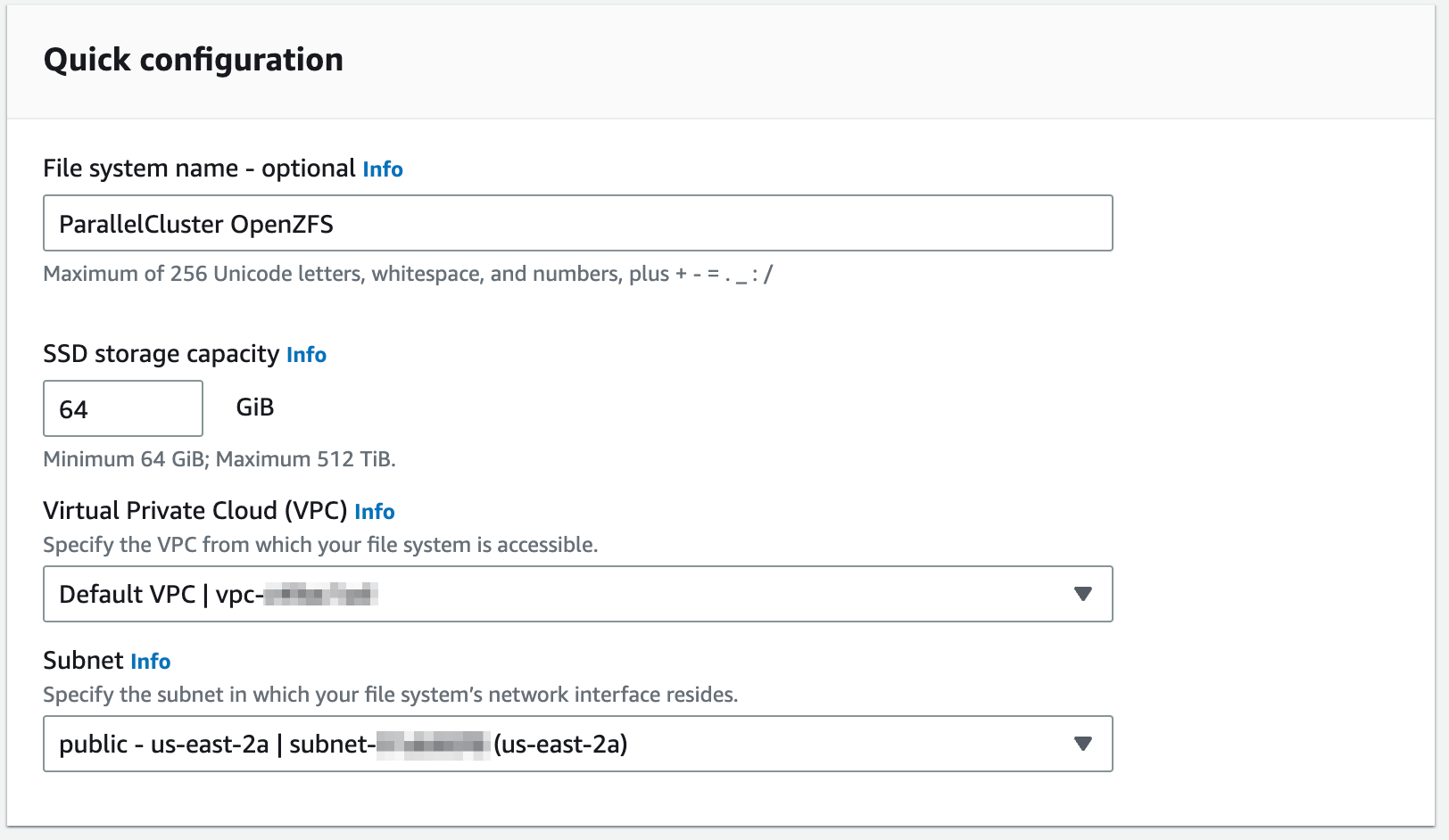
Next give it a name and set the size, (smallest is
64 GB) -
On the next section specify the same VPC and subnet as your cluster.
-
Select the same Security Group you created earlier.
4. Attach Filesystem to AWS ParallelCluster
-
After the filesystem has finished creating, grab the mount command from the Amazon console:
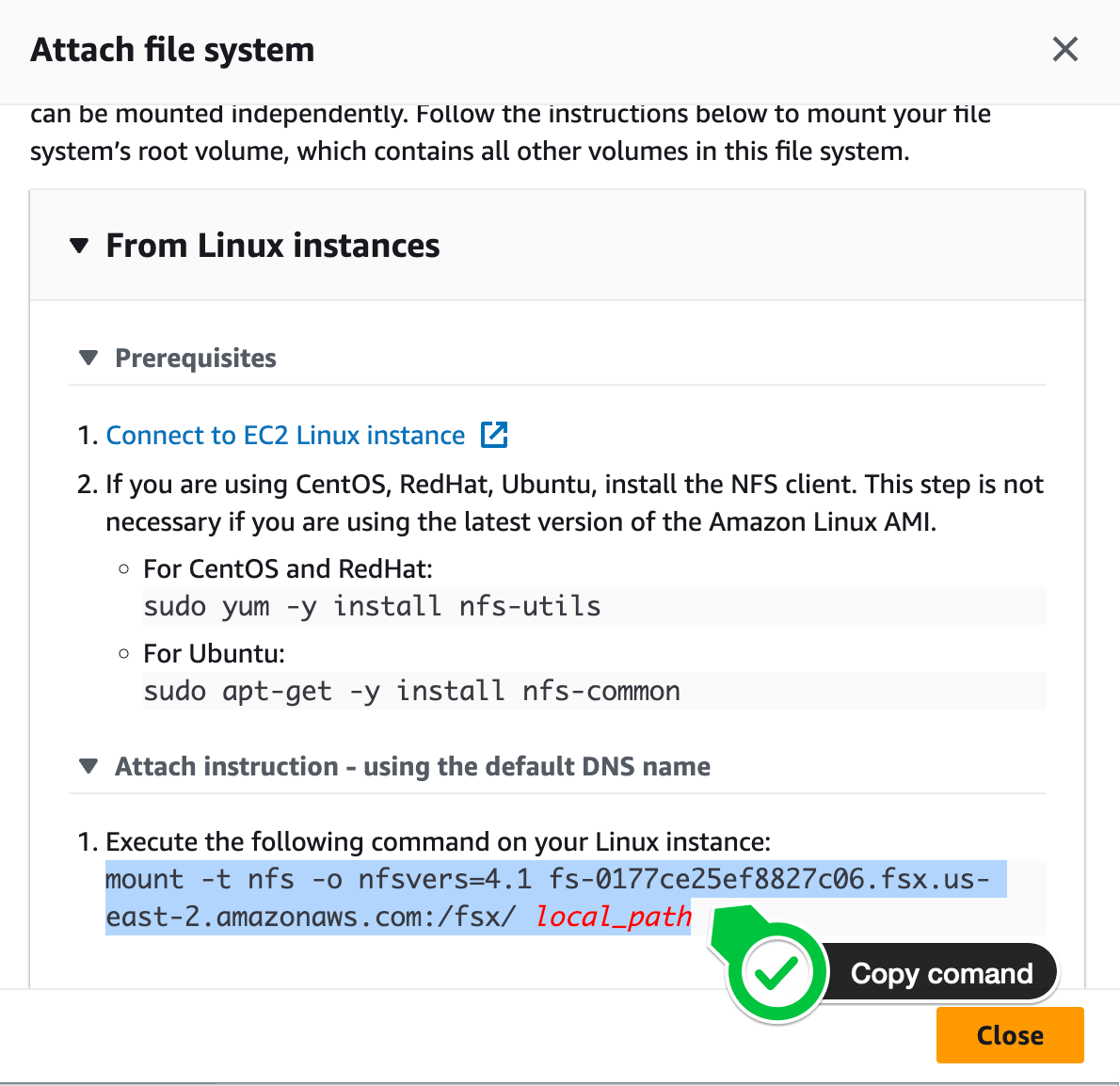
We’ll use the DNS name (including mount dir) to mount the filesystem below.
-
SSH into the HeadNode and create a script
mount-openzfs.shwith the following content:#!/bin/bash # usage: mount-openzfs.sh fs-0177ce25ef8827c06.fsx.us-east-2.amazonaws.com:/fsx /zfs FSX_DNS=$1 MOUNT_DIR=$2 . /etc/parallelcluster/cfnconfig test "$cfn_node_type" != "HeadNode" && exit # create a directory mkdir -p ${MOUNT_DIR} # mount on head node sudo mount -t nfs -o nfsvers=4.1 ${FSX_DNS} ${MOUNT_DIR} cat << EOF > /opt/slurm/etc/prolog.sh #!/bin/sh if mount | /bin/grep -q ${MOUNT_DIR} ; then exit 0 else # create a directory sudo mkdir -p ${MOUNT_DIR} # mount on compute node sudo mount -t nfs -o nfsvers=4.1 ${FSX_DNS} ${MOUNT_DIR} fi EOF chmod 744 /opt/slurm/etc/prolog.sh echo "Prolog=/opt/slurm/etc/prolog.sh" >> /opt/slurm/etc/slurm.conf systemctl restart slurmctld -
Then run it from the HeadNode, specifying the filesystem DNS and mount directory like so:
FSX_DNS=fs-0177ce25ef8827c06.fsx.us-east-2.amazonaws.com:/fsx MOUNT_DIR=/zfs sudo bash mount-zfs.sh ${FSX_DNS} ${MOUNT_DIR} -
To verify that the filesystem mounted properly, you can run
df -h. You should see a line like:df -h ... 172.31.47.168@tcp:/wwu73bmv 1.2T 11M 1.2T 1% /zfs -
Next let’s allocate a compute node to ensure it gets mounted there as well:
salloc -N 1 # wait 2 minutes watch squeue # ssh into compute node once job goes into R ssh queue0-dy-queue0-hpc6a48xlarge-1If all worked properly you should again see:
df -h ... 172.31.47.168@tcp:/wwu73bmv 1.2T 11M 1.2T 1% /zfs